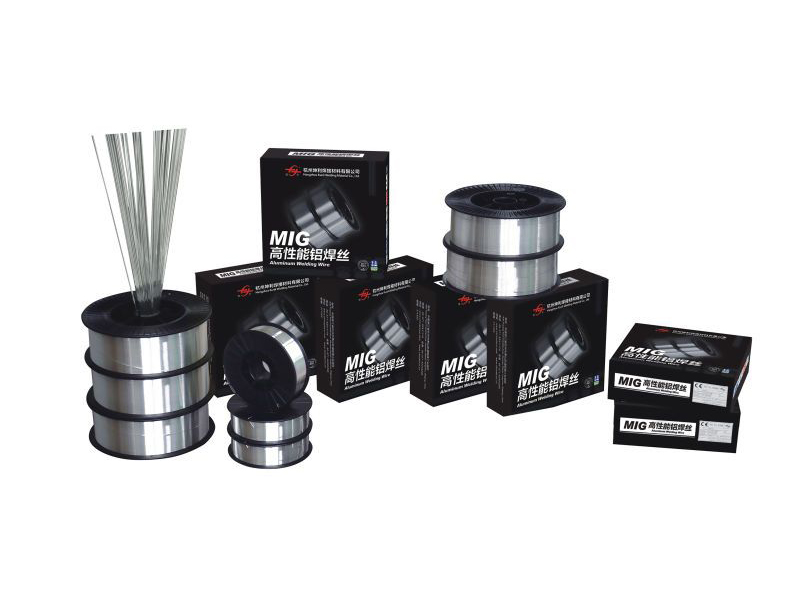
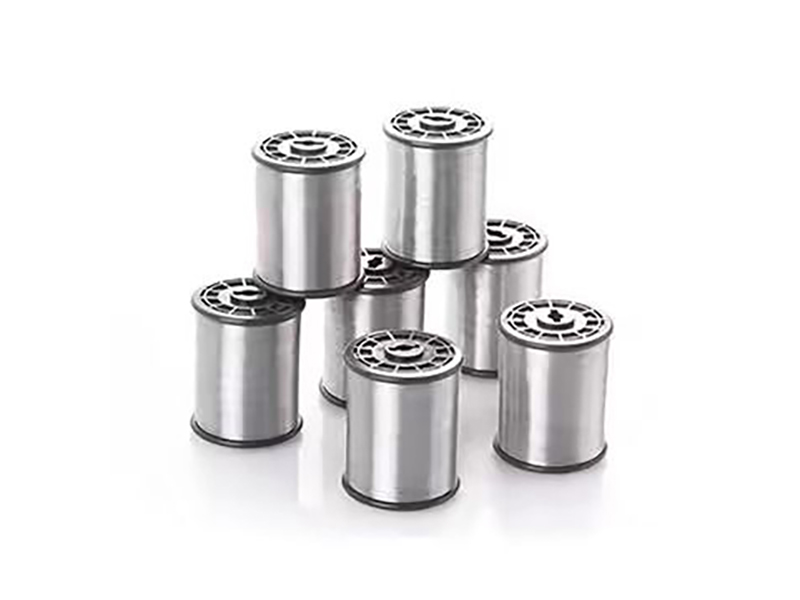
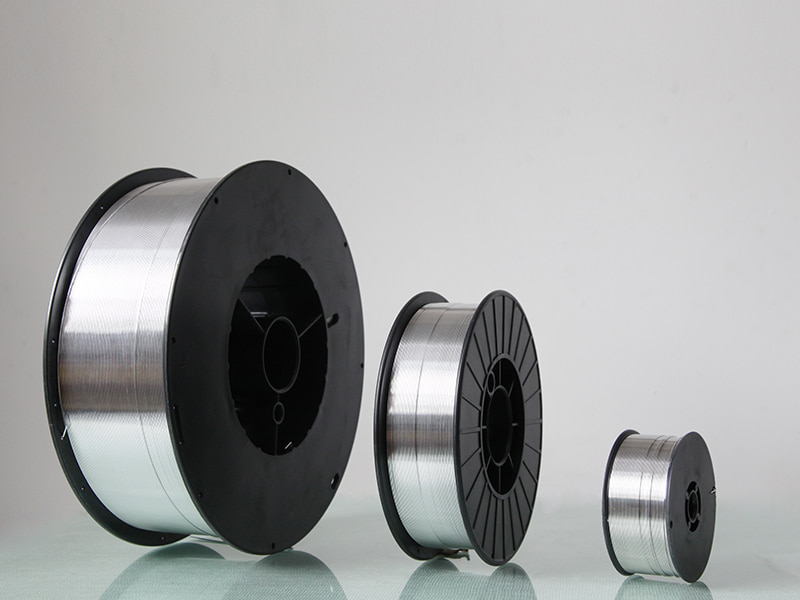
Introduction
The construction of vessels and piping for storing and transporting cryogenic materials (such as LNG, liquid oxygen, and nitrogen) demands weld joints that retain exceptional fracture toughness at temperatures approaching absolute zero. Our specialized 5XXX series filler wires are engineered with controlled Manganese and Magnesium levels to prevent brittleness and maintain mechanical integrity in deep-cold environments. This ensures the long-term safety and reliability of critical cryogenic infrastructure.
Specification
| Classification (AWS) | ER5183 / ER5356 |
| Key Property | Maintained fracture toughness at -196掳C or lower |
| Base Metal Compatibility | 5083, 5456, and other alloys used in cold service |
| Impact Testing | Meets Charpy V-notch requirements at low temperatures |
| Manganese Content | Controlled to optimize low-temperature performance |
Applications
Welding liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage tanks and tankers.
Fabrication of cryogenic air separation units and heat exchangers.
Piping systems designed for liquid hydrogen and oxygen transfer.
Construction of vacuum-insulated cryogenic vessels and dewars.
Payment and Shipping
Material Certificates: Full Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) with chemical and mechanical test results provided.
Logistics: Secure, protective packaging to prevent atmospheric exposure before use in sensitive fabrication shops.
Consultation: Technical consultation available for material selection based on specific operating temperatures.
 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch
 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch